
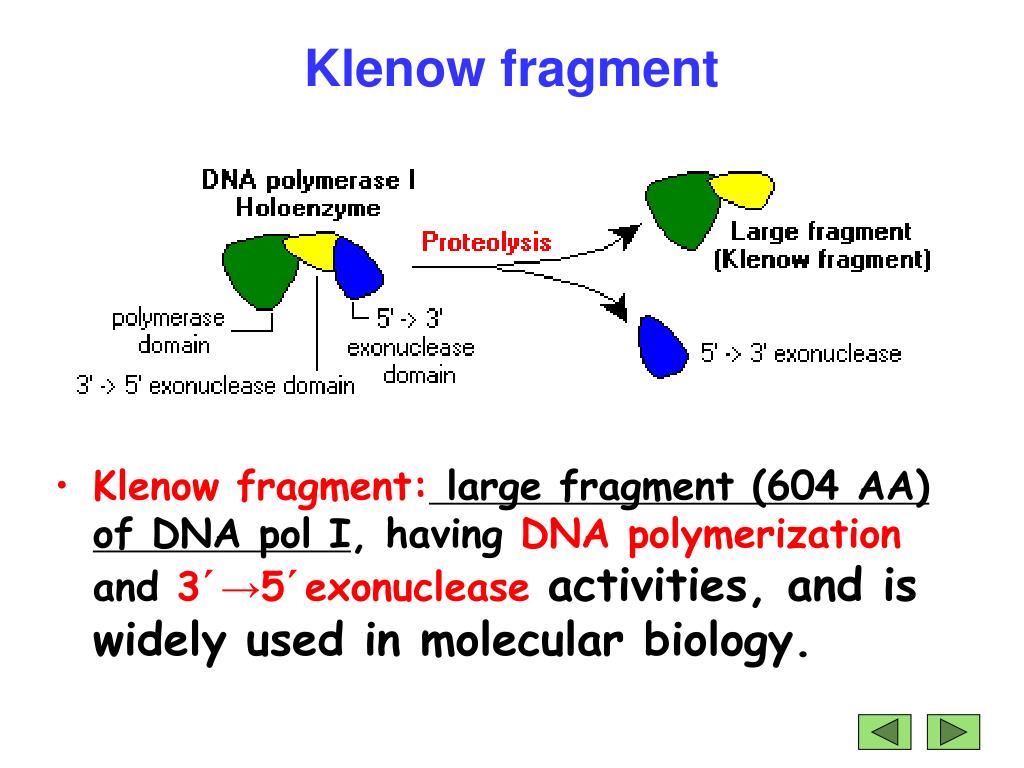
It is very important to use proper conditions to make correct blunt ends. These observations suggest that the positively charged guanidino group in the side chain of Arg682 is catalytically important but not absolutely essential for synthesis of DNA. T4 DNA polymerase, a high concentration of Klenow fragment, a low concentration of DNA fragments, or long incubation time will cause unexpected deletions. coli DNA Polymerase I which retains polymerization and 3 5 exonuclease activity. The reverse mutation of Ala682 to the wild-type form Arg682 fully restored the processive nature and the polymerase activity of the enzyme. DNA Polymerase I, Large (Klenow) Fragment is a proteolytic product of E. The kinetic analyses of the mutant enzymes indicated a 3-4-fold increase in the Km for the substrate dNTP, a 20-25-fold decrease in the Vmax and an overall decrease in the processive nature of DNA synthesis in both the mutant enzymes. Both mutant enzymes showed significantly lower specific activity as compared to the wild-type enzyme. Using this clone (pET-3a-K) as the template, two mutant polymerase clones were constructed in which arginine has been replaced with either alanine, pol I, or lysine pol I. This clone under appropriate conditions overproduces the Klenow fragment in E. coli and was cloned in an expression vector, pET-3a. For this purpose the Klenow-coding region of the DNA-pol-I gene was selectively amplified from the genomic DNA of E. In order to further define the role of Arg682 in the catalytic process, we have performed site-directed mutagenesis of this residue. We have reported that a domain containing Arg682 in the Klenow fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I (pol I) is important for the template-dependent dNTP-binding function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
